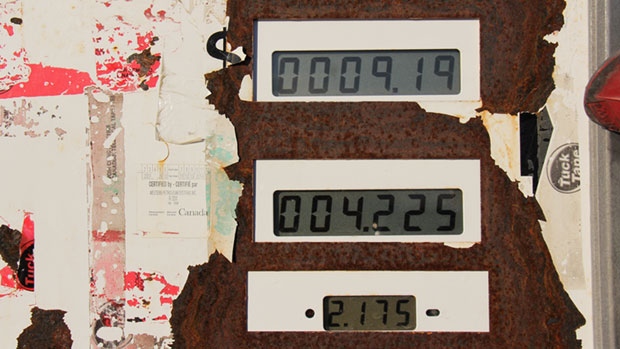by Steve Selden | Feb 26, 2018 | Churchill News
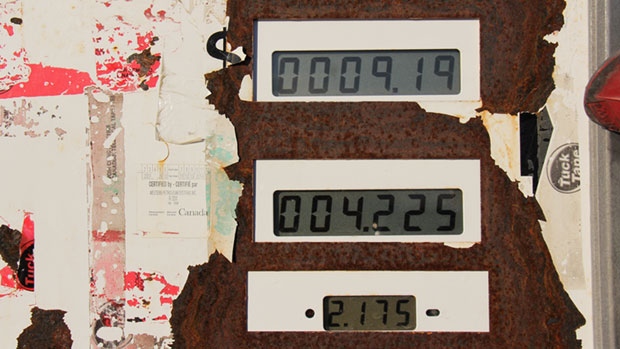
The deMeulles Auto Gas Bar in Churchill reflects the price of gas prior to the rail line washout. Dale deMeulles photo.
Churchill’s gas prices have been reduced by fifty cents a litre thanks to the federal government accessing the economic stimulus fund once again. With petrol prices nearing the $10/gallon mark, this latest reprieve will keep the cost at about $8/gallon. And we complain about gas prices when they reach $3/gallon or more? Kind of puts things in perspective a little, eh?
With federal findings of a probe of Omnitrax, owner of the Port of Churchill facility and the defunct Hudson Bay Line, due to be released soon, residents are enduring rising prices and increased isolation leading to economic strife.
Last week, Natural Resources Minister Jim Carr confirmed that the Ottawa government would allocate $132,870 for Exchange Petroleum to lower gasoline prices to prior levels before the Hudson Bay Rail Line was devastated by flooding last May. Shipping on the railway was the only way to keep costs for supplies and fuel low. Now, ten months later, the pressure is causing long-time residents to move south in search of a more affordable lifestyle.
In September 2016, Ottawa approved the Churchill and Region Economic Development Fund, intended for the diversification of northern Manitoba’s economy following Omnitrax laying off most of the port’s workforce that summer. Businesses have benefitted from the money by offsetting rising shipping costs of materials shipped by barge or airplane.
Last December Carr visited Churchill and announced the government would add $2.7 million to the existing $4.6 million relief fund. After seemingly turning a blind eye to the issue the federal government now is coming to the rescue.
The new windfall of cash will be transferred to Exchange Petroleum, owner of the Calm Air fuel-storage tanks located at the Churchill airport. These tanks are being used due to issues with the port’s storage tanks related to the viability of winter storage of the fuel.

Churchill Port tank farm is unable to store fuel for the town through the winter. Churchill Tank Farm photo.
“This project is a great example of how collaboration and partnerships can help lessen Churchill’s acute economic hardships, restore a quality of life, and keep its entrepreneurs in business,” Exchange CEO Gary Bell wrote in a statement.
Churchill Mayor Mike Spence expressed thanks to Ottawa for its leadership and funding while conveying optimistic thoughts that rail line repairs would commence in the spring.
“This announcement means real savings for residents and businesses of Churchill during these difficult economic times,” Spence wrote. “It’s important to also give a great deal of credit to Exchange Petroleum who stepped in last fall.”
by Steve Selden | Aug 25, 2017 | Churchill News

Hudson Bay line rail damage. CBC photo.
Omnitrax, owner of the Port of Churchill and the damaged Hudson Bay Rail – Line, has apparently obtained an assessment of the severely damaged railroad tracks between Gillam and Churchill. After meeting with Transport Canada officials this past Monday, Omnitrax seems to have a clearer notion of what it will take to repair the tracks.
The company has not yet released the findings and any strategic, updated plan to commence work in the near future. After 13 weeks of inoperability, the Hudson Bay line still sits damaged by spring floods resulting from two historic March blizzards. An August 4th updated engineering report detailing estimated costs for repairs was obtained by Omnitrax though they vowed to divulge the findings only after meeting with Transport Canada.
In early July, repair estimates by Omnitrax ranged between $20 and $60 million which they emphatically stated were “not economically viable”. However, the Canadian government continually insists that the company is responsible via federal transportation laws to keep the lifeline to the north running. Transport Canada, the enforcing agency for the law will not initiate an investigation until it received specific complaints from citizens and other agencies.
Correspondence so far from complainants has not been addressed directly to movement of goods and rail line abandonment prompting responses from some Churchill residents that Ottawa and Omnitrax are dragging their feet in the process. Telling Churchillians they have basically not “complained properly” is not sitting right with many of the distraught residents.

Damaged Hudson Bay rail line. CBC photo.
Churchill Mayor Mike Spence, mayor of Churchill, instead of encouraging residents to file complaints with the regulator has instilled trust in Prime Minister Justin Trudeau. Trudeau pledged he would find a solution on July 28. Trudeau, however, hasn’t said how he plans to proceed.
Home Hardware owner Rhoda deMeulles exemplifies the business owners woes in town by expressing her frustration on lack of supplies due to no cargo arriving via rail. “It’s hard to realize what you need all at once,” said deMeulles, whose store is close to running out of construction supplies and cash.
“We feel like we’re in jail,” said deMeulles, who still loves the town she adopted 38 years ago. “We need help; we need our rail line back.”
Something has to give as the government continues to subsidize groceries for the town. Everyone is expecting a decision by Omnitrax soon, possibly as early as next week.
by Steve Selden | Feb 7, 2017 | Churchill News
In a time when the Canadian Arctic is the focus of energy and trade route exploration, there are human cultural issues that need to be part of the picture as well. Maatalii Okalik, is a young advocate for the ever expanding Inuit youth population and her passion is ensuring all young people of the north will be able to live to the same standards as other Canadians. The 27 – year old is president of Canada’s National Youth Council and her mantra is just that,;“to ensure that Inuit live the same quality of life as fellow Canadians.”
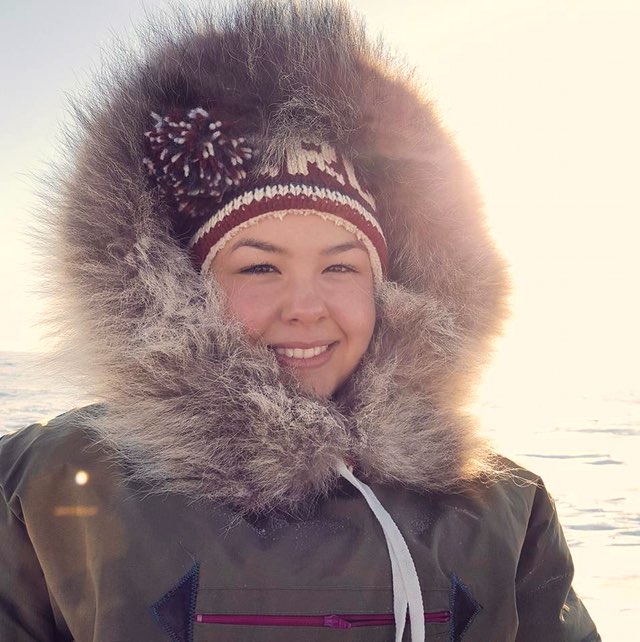

Maatalii Okalik Pres Natl Inuit Youth Council. Maatalii Okalik photo.
Okalik knows the road to Inuit health and education equality will be long and winding and will require hurdling deep – rooted social issues frozen in Canada’s colonial history. Okalik fervently believes that the federal government needs to be more active in revitalizing cultural practices, preserving and facilitating native languages, preventing suicides and upgrading and possibly subsidizing some infrastructure problems.
In Okalik, it appears the Inuit young population will have an inspired advocate for years to come. She was recently bestowed the honor of Indspire Laureate, given to Canadian indigenous professionals and young people demonstrating exceptional achievements in their chosen career. Additionally, Okalik was rewarded with the Qulliit Nunavut Status of Women Council’s Outstanding Young Woman Award!
Arctic Deeply, a northern publication recently interviewed Okalik and she conveyed some pretty informative and interesting thoughts on life in northern Inuit communities. Describing the most pressing concerns and issues of Inuit youth Okalik outlined a basic long – term action plan.
Foremost is the Inuit language -Inuktitut- not being allowed in residential schools. English has been forced upon students therefore degrading the native language of the Inuit people. Okalik contends that federal government in Ottawa should actively push to ensure that Inuit youth should be able to access crucial learning materials in their native language. This would set a basis for equitable education for all Canadians. When the Inuktitut language is watered down the culture will slowly be lost when exposed to the rest of the world.
Secondly, Inuit culture and customs have been identified as an identity crisis currently for Inuit youth. As the youngest, fastest growing population in Canada, Inuit youth are finding cultural practices hard to keep up with. School and work and raising young families impose time and cross – cultural constraints on the continuation of age – old Inuit culture. Youth programming has been seen and proposed as a solution. tradition and modernity need to be woven together more smoothly so to ease the differences between the two.

Inuit children in Pangirtung, Nunavut. Robert Galbraith photo.
The third, and most pressing issue, is suicide prevention in the north within the Inuit population. Inuit suicide rate ranks highest within Canada as well as internationally per capita. Okalik and her colleagues contributed to the national Inuit suicide prevention strategy identifying suicide historical tendencies and plans to control them in Inuit communities.
In all these issues it’s crucial to have Canadians as a whole understand the vast gap in social services whether it be housing, food insecurity, cultural access for youth, education or access to quality and equal health care. With Inuit communities existing on the lower end of the spectrum here, there needs to be help assimilating the people to a better way of life being exposed to them from outside. “To me it just doesn’t make sense for Inuit in our particular communities to be living in Third-World conditions. There should be a priority of Canada to address that inequity. It would be a proactive measure that would prevent some of the dire statistics, including our suicide rates.” states Okalik.
Okalik feels her dreams and definitive career moment will be when all Canadians, including Inuit, enjoy the same quality of life. “I think I’m happiest when I see understanding in someone’s eyes – whether that’s an Inuk youth who learned about the history of colonization, or a federal bureaucrat or high-level minister who decides that this should be a priority and it’s a basic human right.” Then that person might be motivated to try and solve the dilemma and possibly influence policy decisions that might impact Inuit in a favorable manner.
Okalik’s near – term hopes are for the federal government to follow through with the Truth and Reconciliation Commission’s call to action #66 restoring power to indigenous communities all across Canada including most urgently Inuit communities in the Arctic. “The other thing that I think that I’d like to see is the telecommunication of the Canadian Arctic to be at par with southern Canada, including internet and phone. We recognize that these are essential services. It’s not at par in the Arctic. That influences education. It’s really important. Especially when, across the Arctic, we don’t have hospitals in all of the communities. Telehealth for example, is something that’s being explored. We should have access all across the board. As well as internet.”
Lastly Okalik believes that air services across the Nunavut settlements need to become more essential since there are no roads to communities. Many of the social inequities pointed to here are critically impacted by this transportation mode.
by Steve Selden | Jun 6, 2016 | Conservation

The Northwest Passage is becoming newsworthy as a possible Arctic trade route. Fednav photo.
In April China encouraged shippers in country to use the Northwest Passage for trade routes around the world. The problem is there is dispute over the newly, somewhat accessible, Arctic route as to whether it’s an international waterway or under Canadian jurisdiction.
The Northwest Passage is roughly 40 percent shorter than the Panama Canal route, and even though there will be adverse affects on environment and wildlife species, the shorter passage will reduce greenhouse gas emissions by more than 1,300 tons. Russia’s Northern Sea Route has actually drawn more attention since it is usually more navigable than the Northwest Passage, which,often is still impassable throughout the summer. In 2009, only two ships completed the Northern Sea Route voyage as opposed to nearly 500 this year!
Eventually the passage will come to a broader discussion as to who controls rights to the region. However, at this point without enough surety that ships are able to pass with consistency, the issue is at a “simmer” level.
Traditionally, Ottawa and Washington have carried out talks trying to settle the jurisdiction dispute with Canada claiming all rights to the waterways that combine to form the Northwest Passage. Shippers, by this edict, need to comply with Canadian regulations when traversing the passage. The United States disagrees with their proposals but will comply in the meantime and notify Ottawa anytime a US firm plans to sail the waterway. Now with China entering the mix the scales could tip and a cause a flare – up in political negotiations.

The Northwest Passage in the Arctic will be used for future shipping to China. Canadian Geographic image.
China has vaguely outlined its’ own guidelines to sailing the Northwest Passage and announce that it wants more ships utilizing the trade route. In not so many words the country is asserting its position on Canada’s claim.
However, China may just be putting the cart in front of the horse by asserting the trade route preference for the firms that might use the route. COSCO, a prodigious shipper has deemed the northern route too dangerous to attempt on a regular basis.
For now the Panama and Suez Canals still remains the choice for most shipping companies. Posturing is in place by these interested countries for the future and at some point the route will become viable. While weather, year – round ice and challenging navigation conditions are aspects that Ottawa cannot alter, infrastructure and updated mapping can be improved. It seems that regardless of current day usability, the groundwork is being laid for future passage of the mythical region.